-

In-Class Evolution Discussions Change Bible Interpretation
Jessica Abele
Conflict between religion and evolution is a major barrier for religious biology students. Educators have been working to increase evolution acceptance by using a variety of methods (e.g., increasing evolution knowledge, addressing creationism in class, etc.) with little success. However, recent research shows using a reconciliatory approach to evolution and religion increases evolution acceptance while overall religiosity is unaffected (Lindsay et al., 2019).
-

Male and female victims experience different types of sexual assault
Carolyn Allen, Samuel Payne, and Julie Valentine
Intro:
- Sexual assault kits (SAKs) contain forensic evidence and are collected following an assault
- Most research on SAK processing has been done with combined male and female assaults
- 10% of victims are male
- There is lots of research on female victims, but very little research on male victims
-

Chimeric claudins reveal role in neural tube defects
Wesley Allen, Nathan Beckett, Emma Brenchley, Jacob Wengler, Lauren Hall, Cailey Winn, Meredith Mann, Sion Jung, Spencer Thacker, Rachel May, Dario Mizrachi, and Micheal Stark
Claudins (CLDN), a family of proteins found in the tight junction, play a major role in membrane permeability. While claudin disruption is known to contribute to the formation of neural tube defects (NTD), current research methods rely heavily on a non-specific toxin, CPE, when exploring the importance of CLDNs within neural tube formation. This makes it difficult to identify individual CLDN’s contribution to NTD formation, creating a need for a more specific method.
-

Interruption of Junctional Adhesion Molecules Shows Developmental Defects
Wesley Allen, Nathan Beckett, Lauren Hall, Emma Holdaway, Sion Jung, Meredith Mann, Spencer Thacker, Jacob Wengler, Cailey Winn, Dario Mizrachi, and Michael Stark
Development of the central nervous system, the brain and the spinal cord, starts initially with the formation of the neural tube. This vital process starts as a sheet of cells which then folds into a cylindrical structure in the early stages of embryo development (Fig1). Defects in the formation of the neural tube can lead to permanent disabilities in babies after birth. This is important to understand as current statistics show that approximately 300,000 babies are born annually with neural tube defects. (NTDs). In addition to NTDs there are many other dangerous birth defects that are important to understand as we work towards prevention and treatment.
-

Comparison of Tardigrade Extraction Methods
Abigail Andros
It is a time-consuming process to pick tardigrades for an experiment. The standard method is to add water to the sample, then look through it and pick out tardigrades with a micropipette or small wire loop (Tsujimoto et al. 2015).
-
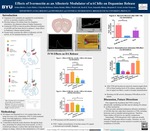
Effects of Ivermectin as an Allosteric Modulator of nAChRs on Dopamine Release
Joshua Barlow, Caylor Hafen, J. Kayden Robinson, Emma Steimle, Hillary Wadsworth, Sarah E. Foote, Samantha Bishop, Benjamin E. Graul, and Jordan Yorgason
- Dopamine (DA) terminals are regulated by acetylcholine activity on nicotinic receptors (nAChRs).
- Nicotine reduces DA release from low frequency stimulation, but enhances release at higher frequencies.
- Ivermectin (IVM) is a known positive allosteric modulator of nAChRs and has been shown to enhance L-dopa effects in Parkinson’s disease animal models.
- Present study examines the effects of allosteric nAChR activity on DA terminal function via IVM.
-

Introducing Xanthoria parietina: Invasive, Naturalized, or Opportunistic?
Mikele Baugh and Steve Leavitt
Lichens are one of the world’s ubiquitous group of organisms. They have been documented from frigid tundras to arid deserts. While some species are known to be particularly hardy and flexible in their habitats, many species are linked to specific growing conditions. As the global climate changes, the geographical range for different growing conditions shifts. Economic trade and human travel provide new opportunities for species to access new locations that are beginning to develop habitable conditions. Xanthoria parietina has been observed in the Great Basin (a region outside of its typical coastal distribution) found in newly built horticultural landscapes. Individuals that are introduced are found to only survive a year or two before dying. A specimen found on BYU campus is believed to be the only observed individual to have persistent growth for more than a decade.
-

The Role of CD5 in CD4+ T cell Metabolism
Joshua Bennett, Kiara Whitley, Claudia Freitas PhD, Christopher Haynie, Carlos Moreno, and Scott Weber
T cells serve a key role in the immunological response in the adaptive system. Different receptors present on the T cell have certain roles and are able to either inhibit or stimulate signaling which consequently regulates the function and metabolism of the cell. CD5 is an inhibitory co receptor expressed on the surface of T cells known to regulate thymocyte selection and TCR signaling . Our goal is to better understand the effects of CD5 regulation in metabolism. Using metabolic flux assays, we found that CD5KO naïve T cells have increased glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration in comparison to wild type naïve T cells. Using GC MS, significant differences in amino acid levels in both the T cells and the serum of CD5WT and CD5KO mice were identified. Understanding the metabolism of CD5 regulation could elevate our knowledge of immunotherapies and adaptive immune responses in treating diseases like cancer.
-

Potential Regulation of Breast Cancer Invasion by Thymidine Kinase 1
Eliza E. Bitter, Rachel M. Morris, Toni O. Mortimer, Kai Barlow, Abigail Schekall, Michelle H. Townsend, Jonathan Skidmore, Brett E. Pickett, and Kim L. O'Neill
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women and is largely treatable within the early stages of the disease. However, patient mortality drastically declines as the tumor begins to invade other tissues and metastasize, making aggressive phenotypes especially problematic to treat. Such treatment typically requires an aggressive and decisive multidisciplinary approach. The recent expansion of immunotherapy as a viable treatment option has greatly improved treatment outcomes, especially with aggressive breast cancer phenotypes. Thymidine kinase 1 (TK1) is a DNA salvage pathway enzyme that is highly expressed during S phase and involved in cell cycle repair. Past studies indicated that TK1 is secreted into the serum of cancer patients and that its upregulation is an early event in tumorigenesis, thus suggesting that TK1 upregulation may have potential importance in tumor progression.
This study’s objective was to further elucidate TK1’s role in tumor progression and metastasis of breast cancer specifically. We hypothesized that TK1 overexpression in breast cancer may affect invasion. To investigate this, TK1 mRNA transcript levels were analyzed between normal and BRCA patient tissue samples. The wild-type breast cancer cell line HCC 1806 was used, as well as a TK1 knockdown (L133) which was produced using CRISPR-Cas9. Successful TK1 knockdown was verified through western blot and qPCR. Bioinformatics was also performed to analyze the relationship between our breast cancer cell lines and various cell adhesion factors. The cell lines HCC 1806 and L133 were then tested with an invasive scratch assay. Additional western blots were run to further investigate the potential relationship TK1 may have with other cell cycle checkpoint proteins. Results showed that TK1 mRNA transcript levels are higher in BRCA tissues compared to normal controls. Western blot and qPCR indicated that TK1 was successfully knocked down in L133 cells. Bioinformatic differential gene analysis revealed several correlations with cell adhesion factors, with contrasting correlations when compared between the HCC 1806 and L133 cell lines. The invasive scratch assay results indicated that the TK1 knockdown L133 cells were less invasive than HCC 1806 cells.
In conclusion, results verified that TK1 is highly expressed in breast cancer and that it may help tumor invasion by influencing cell adhesion factors. Further investigation to understand TK1’s potential interactions with important cell adhesion factors, such as FHL1 or GAS6, may help elucidate other therapeutic targets for preventing disease progression.
-

Does Bathing After Sexual Assault or Time Elapsed Have a Greater Effect on the Development of CODIS Eligible DNA Profiles?
Emily Black, Sam Payne, Julie Valentine, and Leslie Miles
Which has a greater effect on the development of CODIS eligible DNA profiles from SAKs – bathing/showering status of the victim or time between the assault and examination?
-

The Unseen Burdens of Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension: Treatment Side Effects and Access to Care
Rebecca Brown, Megan Pierce, Samara Nelson, Ashley Bangerter Seelos, Ella Cook, Heather Stickle, Michael Johansen, and Erik J. Nelson
- Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a serious and life-threatening disease characterized by an elevation in mean pulmonary artery pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance, leading to right heart failure and death.1,2
- PH has primarily been studied among adults and therefore clinical therapies have also aimed at treating this population.3-5
- Several pharmaceutical treatments are available and approved for use in adults, however, the effectiveness among children has yet to be sufficiently determined though they are considered the standard treatment regimen in children.
- Accessing specialized pediatric PH care providers who are versant in these therapies is difficult.
-
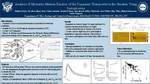
Analysis of Michaelis-Menten Kinetics of the Dopamine Transporter in the Striatum Using Iontophoresis
Matthew Burris, Ali Allred, Emma Read, Joakim Ronstrom, Brayden Tolman, Anna Everett, Hillary Wadsworth, Jared Willets, Eliza White, Matthew Rasmussen, and Jordan Yorgason
- - Dopamine (DA) is a major neurotransmitter responsible for reward and motivation
- Reuptake of DA occurs through the dopamine transporter (DAT)
- Cocaine: DAT antagonist
- Purpose: to develop a model that measures the Michaelis Menten (MM) kinetics in the dorsal striatum (DS) to determine the K m and V max for the DAT
-

The development of a rhizobia seed coating to establish lupine species to reclaim minelands and degraded rangelands
Bridget Calder, Curtis Drake, Alex Benedict, Joel Griffitts, Brad Geary, Chris Miller, April Hulet, Kate Ruebelmann, Danny Summers, and Matthew Madsen
The establishment of native plants in degraded landscapes proves difficult because of a lack of healthy soils and nutrient availability. Rhizobia are nitrogen-fixing bacteria found naturally in the soil. Legume plants can form symbiotic relationships with these bacteria. Plants provide carbohydrates for the bacteria, while in turn, the bacteria fixes atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia – a form that the plant can use. By coating legume species with these beneficial bacteria, they can grow in soils with low plant-available nitrogen. Seed coating technology allows for the efficient delivery of rhizobia at the time of planting.
-

Predation history has no effect on lateralized behavior in Brachyrhaphis rhabdophora
Maren Callaway, Erik S. Johnson, and Jerald B. Johnson
Lateralized behavior is common in nature: sea turtles preferentially use a dominant flipper to swim, passerine birds display footedness when catching mealworms, and humans display a bias in head-turning during kissing. Several fish species even prefer to use one eye over the other when viewing certain stimuli.
Predation is an environmental factor known to affect behavior in a variety of organisms (e.g., mule deer, water striders, and some species of Poeciliid fishes). Mosquitofish males, for example, preferentially use one eye to evaluate mates and predators, but show no bias for other males or an empty tank
-

Estradiol effects on dopamine release and cholinergic interactions
Joseph Carroll, Marcus Perkins, Whitney Cook, Laird Busselburg, Lillian Brady, Erin Calipari, Zak Estrada, and Jordan T. Yorgason
Dopamine release in the striatum is regulated by intrinsic activity as well as local cholinergic interneurons. Dopamine terminals express nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR), including a4~2 receptors that are sensitive to sex hormones. These receptors are also activated by acetylcholine release from cholinergic interneutons that is sufficient for driving dopamine relelase independent on dopamine somatic firing. The present study examines cholinergic mediated dopamine release and the sex hormone estradiol.
-

The Effects of Exercise on Hunger and Satiety Hormone Concentrations Over a 36-hour Fast
Coleton J. Chamberlain, Garrett Lance, Jacob L. Coleman, Landon S. Deru, and Bruce W. Bailey
Food intake and metabolism are often key indicators for the onset of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease and cancer (1). Food intake is largely regulated by hormones that signal satiety and hunger (2). Current literature has shown that exercise reduces food seeking behaviors. (3) These hormones include ghrelin, which stimulates food intake, and GLP-1, leptin, PP, and PYY, which all create a satiation effect and reduce food seeking behaviors. We hypothesized that a bout of intense exercise at the beginning of a 36-hour fast would reduce the secretions of hunger hormone ghrelin and increase the concentration of satiety hormones GLP-1, PP, PYY and leptin.
-

Preventative Practices and Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Caregivers of Children with Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension
Ella Cook, Megan Pierce, Samara Nelson, Ashley Bangerter Seelos, Rebecca Brown, Heather Stickle, Michael Johansen, and Erik J. Nelson
- Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) is characterized by issues of lung growth and development prenatally and postnatally.1
- COVID-19 causes endothelial dysfunction, hypoxia and vasoconstriction. Children living with PH are especially vulnerable to severe complications from the virus due to these additive affects on a cardiorespiratory system that is already stressed by their underlying disease2
- Parents/Caregivers of children with PH have a great burden to prevent COVID-19 infection.
-

Assessing the effectiveness of cattle exclosures on spring within the Escalate River watershed
Lauryn Crabtree
- Springs provide some of the only water and vegetation resource to all life in the Utah desert and are considered fragile ecosystems
- These are significant to the ancestorial heritage of indigenous tribes and early pioneer settler descendants
- Cattle grazing on public lands poses as a threat to spring stability and all life that depends on it
- Tribal leaders, cattle ranchers, and government agencies currently conflict with one another over spring management.
- Finding solutions that meet the middle ground of all these groups is critical in responding to this issue timely
- The agencies have currently implemented fencing to exclude cows from entering a spring called “ exclosures
- There has not been much research done regarding if this management practice is effective in protecting springs
-

QTL analysis of floral traits in a novel interspecies cross in Gilia
Joseph DeTemple and Clinton Whipple
Conclusions
- Inflorescence Traits depend on several genetic loci
- Flower morphology can be explained by PCA analysis
- Many floral traits are highly correlated, suggesting evolutionary constraint
-

The Effects of Exercise on Inflammatory Biomarkers over a 36-h Fast
Austin F. Duersch, Bruce W. Bailey, Landon S. Deru, Jacob Coleman, Hunter Chamberlain, and Spencer Cleverly
Diet-induced chronic inflammation has become a popular point of discussion over recent years in lifestyle medicine as studies have uncovered the effects that inflammation markers have on chronic diseases including heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Each time we eat, an immune response is stimulated resulting in increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers.1,2 Interventions to help lower inflammation could help promote longevity and decrease risk of chronic diseases. This study assessed the impact of an acute 36h fast with and without exercise at the beginning on inflammatory biomarkers IL-6, C-peptide, GIP, MCP-1, and TNF-alpha.
-

Impact of Megafire on Aquatic Insect Communities in Central Utah
Anna Eichert, C. Riley Nelson, and Paul Frandsen
In 2018, a 610-km² megafire complex and residual storms following Hurricane Rosa triggered flash flooding and debris flows throughout the Spanish Fork River (Utah) watershed. The size of the megafire allows for the testing of multiple hypotheses about ecosystem recovery across elevational diversity and vegetation gradients.
-

Effects of immune system activity and methamphetamine on dopamine terminal function
Lauren Ford, Sara Linderman, Hillary Wadsworth, and Jordan Yorgason
- Dopamine (DA) release in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) is associated with addiction and reward • Microglia are native macrophages that act as the immune system of the brain
- Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are bacteria-derived endotoxins that trigger an immune response through microglial activation
- The dopaminergic drug methamphetamine can also target microglia, but produces feelings of reward rather than feelings of sickness
- Present study examines the modulatory effect of microglial activation on dopamine terminal function in the presence of methamphetamine
-

Microbial Health Implications of Evaporative Coolers
Sterling Fuller, Jaxon Tadje, Jim Johnston, and Scott Weber
Evaporative Cooling is one of the oldest and most energy efficient methods of air conditioning used in dry, arid environments The diagram below shows how these machines function by drawing hot, dry ambient air across a wet evaporative pad, effectively cooling the interior environment as sensible heat is transferred to latent heat in the form of water vapor In this study we explore how evaporative coolers ( may distribute unique bacteria into homes through microbial growth propagated in the sump water There is evidence that this diverse microbial environment provided by ECs may confer early life immunological protection against the development of allergies and asthma 1 2 Specifically, previous investigations have shown higher levels of endotoxin in dust from homes with ECs compared to homes with central air conditioning units Endotoxins are found on gram negative bacteria, and have been shown to significantly affect respiratory health and development High through put DNA sequencing of the V 1 V 2 region of the 16 s rRNA gene allows us to identify, categorize and analyze these different bacterial and archaeal taxa found in homes utilizing different air cooling methods
-

How does student ethnicity influence student science identity in undergraduate biology classes?
J. Gaspar de Alba, Samara Nichols, and E. G. Bailey
Science identity and ethnic identity interact in a complex way that varies student to student. However, NHPI students' ethnic identities are typically strengthening to their science identity
-

Polymer Coated Urea Microplastics: Sweet Corn
Benjamin T. Geary, C. J. Seely, and B. G. Hopkins
• Polymer Coated Urea (PCU) is beneficial for providing the food, fuel, and fiber needed for the nearly 8 billion people on earth.
• Microplastics, from a wide range of waste materials, pollute water bodies.
• One potential source of microplastics are from PCU fertilizers if the coatings are transported overland into water bodies.
• Various agricultural application methods vary in potential for surface runoff.
Objective • Determine the microplastic concentrations from runoff water for strip injection, surface unincorporated, and broadcast incorporated application in sweet corn.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

